A sustainable solution for a thirsty planet”
Headlines from around the world tell us stories about water shortages, famine, and disease. The only solution is water desalination.
What is water desalination?
Desalination is a process of separating the dissolved salts from the sea water.
There are various stages in Water Desalination. They are
- Sea water intake
- Pretreatment
- Post – treatment
- Reverse osmosis
- Polishing
- Brine disposal
Sea water intake
The various types of sea water intake are
Open intake
Surface water intake
Beach wells – Best suited for areas, where sea water quality varies; where high turbidity occurs.
Desalination pretreatment
If the sea water is left untreated before Reverse Osmosis, it may cause fouling. Fouling is the accumulation of particles in the membrane as shown in the picture.
Why is pre – treatment necessary?
In the absence of pre – treatment, the membrane surface gets accumulated by the filtered particles, eventually dropping the membrane productivity and increases the operational cost.
The following treatment processes are used to avoid fouling.
| Pre – treatment used | Cause | Fouling prevented |
| Filtration | Clay, sand, suspended solids | Particle fouling |
| Chlorination | Viruses, Bacteria, protozoan, micro – organisms | Bio – fouling |
| Coagulation & FiltrationOptional : Flocculation & Sedimentation | Micro – algae, Colloidal particles | Colloidal fouling |
| Coagulation, filtration, activated carbon adsorption | Natural Organic Matter : bio – polymers | Organic fouling |
| Antiscalant dosing | Sulphates and carbonates of calcium, magnesium, Strontium | Mineral fouling |
| Oxidant scavenger dosing | Chlorine, Ozone | Oxidant fouling |
Chlorination
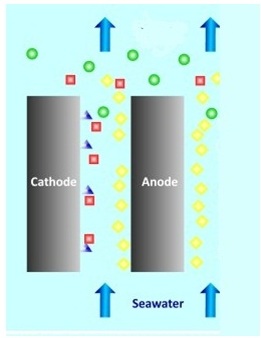
Chlorination is adding chlorine to water. For a small scale plants, sodium hypo – chloride is added. Medium scale plants chlorine gas is forced into the water. When chlorination is done on a large scale, electro – chlorination method is used.
At anode – 2Cl → Cl2 + 2e–
At cathode – 2Na+ + 2H2O + 2e–→ 2NaOH + H2
In the electrolyte – 2NaOH + Cl2 → NaCl + NaOCl + H2O
Over all reaction – NaCl + H2O + 2Cl → NaOCl + H2 ↑
In the picture, yellow balls are the chlorine, green balls are NaOCl, red is NaOH, and the blue triangles are NaOH
Coagulation
Small particles cannot be removed by sedimentation as they do not settle down to the bottom. Such small sized particles are made to a larger chunk by coagulation
A chemical like alum, is added to the sea water. Alum produces positive charges that neutralize the negative charges in the sea water. As the charges stick together, large particles are formed.
Flocculation
In this process, water is passed through a tank with churning paddles. Mixing is done slowly in flocculation step. As the paddles turn the water, the suspended particles start rotating. Due in course, they stick to each other.
Sedimentation
Settling of large particles is called sedimentation.
Reverse Osmosis
The core process of Water Desalination is reverse osmosis. The following are the main requisites of the process
- High Pressure pump.
- Energy recovery device
- Reverse Osmosis Membranes
The sea water is pressurised by the high pressure pumps, before the water enters the membranes. The pressure of the pump is typically between 55 bars and 85 bars.